Spring-boot Api to Upload a File With a Few Meta-data Fields.
In this article we will look at uploading file with Bound Kicking . Uploading and downloading files are a common task for whatever web awarding. In this commodity we volition acquire the process to upload and download files using Bound Boot uploading a file in Spring MVC. We will see how Jump Kick can help us speed up the process.
Introduction
If yous are working in web development, chances are that you may have already worked on file upload or download feature in your awarding.Bound Kick provides a pluggable architecture for the file upload feature.MultipartResolver from theorg.springframework.web.multipart package is a strategy for parsing multi-part requests, including file uploads. At that place is one implementation based on Commons FileUpload and another based on Servlet 3.0 multi-role asking parsing. Nosotros will build our application in 2 parts.
- A web application to upload and download file using a web interface (Will apply Thymeleaf to build UI).
- Residual APIs for uploading and downloading files.
1. Setting up Application.
Let'due south start by creating the web awarding. We tin use the IDE or Spring Initializr to bootstrap our application. We are using Spring Initializr for this post every bit it offer a fast way to pull the dependencies to build our application.
- Go to https://outset.spring.io/.
- Select the web and Thymeleaf every bit dependencies.
- Fill information for the group and artifact and click on the "Generate" push.
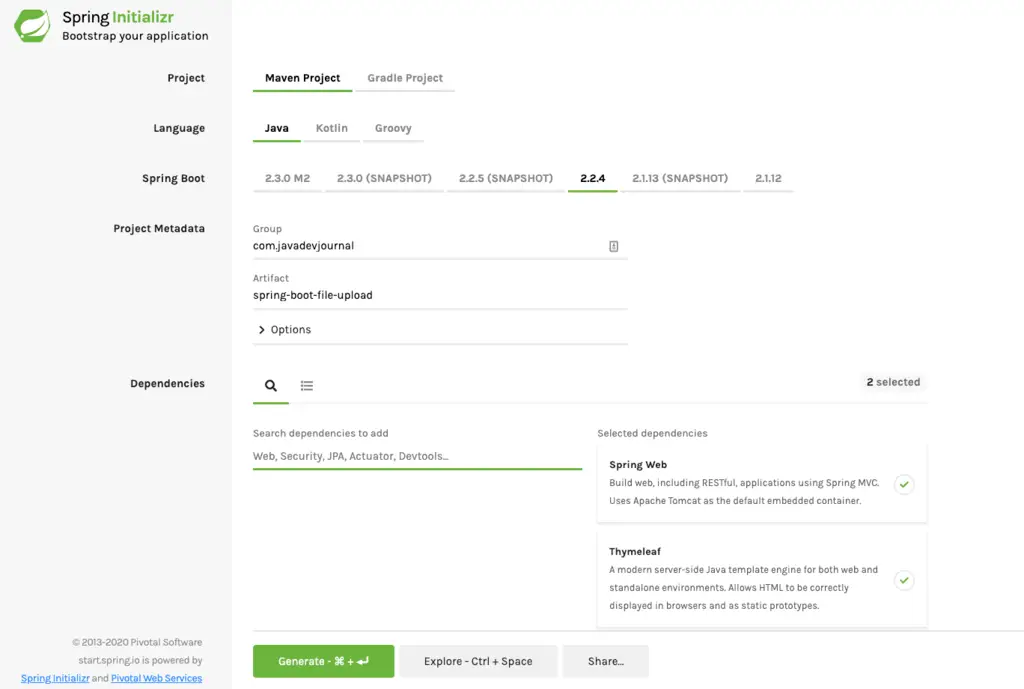
Unzip and import the maven project in your IDE. If you like to use the Spring Kicking CLI to generate the project structure, run the post-obit command from the final.
$ bound init --proper name spring-kicking-file-upload --dependencies=spider web,thymeleaf bound-kick-file-upload Using service at https://start.spring.io Project extracted to '/Users/jump-boot-file-upload' Hither is our pom.xml<lawmaking> file for the awarding:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/four.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-case" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>iv.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.kicking</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.ii.4.RELEASE</version> <relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <groupId>com.javadevjournal</groupId> <artifactId>jump-boot-file-upload</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>jump-boot-file-upload</name> <description>Sample application to upload and download file using Spring Boot</description> <backdrop> <coffee.version>i.viii</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>leap-kick-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.kicking</groupId> <artifactId>spring-kicking-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.kicking</groupId> <artifactId>jump-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId> <artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.kick</groupId> <artifactId>bound-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project> 2. Jump Kicking Chief Class
Jump Boot provides a flexible mode to kickoff our web application using the standard primary method. For not kick application, we demand to register a MultipartConfigElement simply spring kicking auto-configuration volition practise this automatically for us.
parcel com.javadevjournal; import org.springframework.kick.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.kicking.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication public class SpringBootFileUploadApplication { public static void chief(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringBootFileUploadApplication.class, args); } } 3. File Uploading Configurations
Let's fine tune the file upload properties for our awarding using application.properties file. Open up src/primary/resource/application.properties file and change the following properties as per your application need.
#Whether to enable support of multipart uploads.default is true #jump.servlet.multipart.enabled =true # All files uploaded through will be stored in this directory file.upload-dir=/Users/javadevjournal/uploads #Threshold after which files are written to deejay.default is 0B bound.servlet.multipart.file-size-threshold = 3KB #Max file size.Default is 1MB spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size= 2MB #Max request size.Default is 10MB spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size= 20MB #Whether to resolve the multipart request lazily at the time of file or parameter access.Default is false spring.servlet.multipart.resolve-lazily=true In the first part, we volition create a file upload awarding using Thymeleaf while the 2nd half, we will build file upload and download using Remainder API.
iv. File Upload/Download Controller
The starting time function of our awarding is to create a file upload controller. Our controller will take the functionalities to upload and download files also store the file in temp location.
packet com.javadevjournal.controller; import com.javadevjournal.information.FileMetaData; import com.javadevjournal.exception.FileStorageException; import com.javadevjournal.service.FileStorageService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders; import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.ui.Model; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.notation.PostMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile; import org.springframework.spider web.servlet.mvc.support.RedirectAttributes; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; @Controller public grade FileUploadController extends PageController { @Autowired FileStorageService fileStorageService; /** * Controller to brandish the file upload class on the frontend. * @param model * @return */ @GetMapping("/upload-file") public String uploadFile(final Model model) { return "uploadFile"; } /** * Mail method to accept the incoming file in the application.This method is designed to take * just one file at a time. * @param file * @param redirectAttributes * @render succes page */ @PostMapping("/upload-file") public Cord uploadFile(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file, RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes, Model model) { try { FileMetaData data = fileStorageService.store(file); information.setUrl(fileDownloadUrl(data.getFileName(), "/media/download/")); model.addAttribute("uploadedFile", data); } catch (FileStorageException e) { model.addAttribute("error", "Unable to shop the file"); return "uploadFile"; } render "uploadFile"; } /** * Controller to allow customer to download the file by passing the file name as the * request URL. * @param fileName * @param response * @return * @throws FileNotFoundException */ @GetMapping("/media/download/{fileName:.+}") public ResponseEntity < Resource > downloadFIle(@PathVariable String fileName, final HttpServletResponse response) throws FileNotFoundException { FileMetaData fileData = fileStorageService.getFile(fileName); response.setContentType(fileData.getMime()); return ResponseEntity.ok().header(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_DISPOSITION, "attachment; filename=\"" + fileName + "\"").body(fileData.getResource()); } } I accept added the comment to the controller for clarity. Our controller is using the FileStorageService for storing files in the file system (Nosotros will make some changes to store some data in the database in the second role of this commodity.). The FileStorageService service returning the FileMetaData equally a response.
4.1. FileMetaData.
This data course contains the standard data for the file in the system. This is how our FileMetaData class look like:
parcel com.javadevjournal.data; import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; public course FileMetaData { private String fileName; private String url; individual String mime; individual long size; private Resource resources; public FileMetaData() {} public FileMetaData(Cord fileName, String url, Cord mime, long size) { this.fileName = fileName; this.url = url; this.mime = mime; this.size = size; } //getter and setter methods. } 4.2. File Storage Service.
To store and retrieve the files from the file arrangement, let'south create our FileStorageService. Our file storage service class will help united states:
- Store the file in the file organisation and return the stored file metadata data.
- Procedure the stored file data for the download.
- Characteristic to delete the file.
We volition keep this course short for the post, but you can extend it as per your requirement.
bundle com.javadevjournal.service; import com.javadevjournal.data.FileMetaData; import com.javadevjournal.exception.FileStorageException; import com.javadevjournal.utils.UploadFileProperties; import org.apache.tika.notice.Detector; import org.apache.tika.io.TikaInputStream; import org.apache.tika.metadata.Metadata; import org.apache.tika.mime.MediaType; import org.apache.tika.parser.AutoDetectParser; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.beans.mill.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; import org.springframework.core.io.UrlResource; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import coffee.net.MalformedURLException; import coffee.nio.file.Files; import java.nio.file.Path; import java.nio.file.Paths; import java.nio.file.StandardCopyOption; import java.util.Listing; @Service("fileStorageService") public course DefaultFileStorageService implements FileStorageService { private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DefaultFileStorageService.class); @Autowired UploadFileProperties uploadFileProperties; @Override public FileMetaData store(MultipartFile file) throws FileStorageException { //Normalize the path past suppressing sequences like "path/.." and inner unproblematic dots. String fileName = StringUtils.cleanPath(file.getOriginalFilename()); effort { // nosotros can add additional file validation to discard invalid files Path uploadDir = getUploadDirLocation().resolve(fileName); //copy the file to the upload directory,it will replace whatever file with aforementioned name. Files.copy(file.getInputStream(), uploadDir, StandardCopyOption.REPLACE_EXISTING); FileMetaData fileData = new FileMetaData(); fileData.setFileName(fileName); fileData.setSize(file.getSize()); fileData.setMime(file.getContentType()); return fileData; } catch (IOException e) { LOG.error("unable to cpy file to the target location {}", east); throw new FileStorageException("Unable to store file " + fileName); } } /** * Read all files and return as list of @FileMetaData * @return */ @Override public List getAllFiles() { return nix; } /** * Method to return the file every bit @Resources for the download.It read the file from the file system * and return information technology as @Resource * @param fileName * @render FileMetaData * @throws FileNotFoundException */ @Override public FileMetaData getFile(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException { Path path = getUploadDirLocation().resolve(fileName).normalize(); attempt { Resources resource = new UrlResource(path.toUri()); if (resource.exists()) { Metadata metadata = getFileMetaDataInfo(resource); FileMetaData fileMetaData = new FileMetaData(); fileMetaData.setResource(resources); fileMetaData.setFileName(fileName); fileMetaData.setSize(metadata.size()); fileMetaData.setMime(metadata.get(Metadata.CONTENT_TYPE)); return fileMetaData; } else { throw new FileNotFoundException("Not able to discover file"); } } catch (MalformedURLException e) { throw new FileNotFoundException("Not able to find file"); } } /** * Provides the upload directory location based on the awarding.properties configurations * * @render Path */ private Path getUploadDirLocation() { return Paths.go(uploadFileProperties.getUploadDir()).toAbsolutePath().normalize(); } /** * Helper method to get the file meta-data using Apache Tikka corre library.JDK as well provide * way to read meta-information information just it's very limited and take lot of bug. * @param resource * @return Metadata */ private Metadata getFileMetaDataInfo(Resource resource) { AutoDetectParser parser = new AutoDetectParser(); Detector detector = parser.getDetector(); Metadata metadata = new Metadata(); try { metadata.ready(Metadata.RESOURCE_NAME_KEY, resource.getFile().getName()); TikaInputStream stream = TikaInputStream.get(resource.getInputStream()); MediaType mediaType = detector.detect(stream, metadata); metadata.set(Metadata.CONTENT_TYPE, mediaType.toString()); } catch (IOException due east) { e.printStackTrace(); //fallback to default content blazon metadata.set(Metadata.CONTENT_TYPE, "application/octet-stream"); } render metadata; } } Nosotros are using standard JDK feature to write the data on the file system. For file meta-information; I am using Apache Tikka core library every bit JDK built-in features are very express and contains a lot of issues. To utilise Tikka core, add following dependency in your pom.xml file:
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.tika</groupId> <artifactId>tika-core</artifactId> <version>one.23</version> </dependency> 5. Excepton Classes.
We are using the mix of custom and JDK exception classes to handle exceptional scenario:
-
FileStorageException– Exception thrown by API during file storage operation. -
FileNotFoundException– In case the requested file is not available in the file arrangement.
five.1. FileStorageException
package com.javadevjournal.exception; public class FileStorageException extends Exception { public FileStorageException() { super(); } public FileStorageException(String message) { super(message); } public FileStorageException(Cord message, Throwable cause) { super(bulletin, cause); } } vi. HTML For File upload.
Let's build a simple HTML to permit end user to upload and download the files. Create an HTML file uploadFile.html in the src/chief/resources/templates directory.
<html xmlns:thursday="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <body> <div thursday:if="${uploadedFile}"> <h2> Uploaded File Details </h2> <table> <tr> <td th:text="${uploadedFile.fileName}">File Name</td> <td thursday:text="${uploadedFile.mime}">File Type:</td> <td thursday:text="${uploadedFile.url}">URL :</td> </tr> </table> </div> <div> <h2> Uploaded New File </h2> <form method="POST" enctype="multipart/form-data" action="/upload-file"> <tabular array> <tr> <td>File to upload ane:</td> <td><input type="file" name="file" /></td> </tr> <tr> <td></td> <td><input blazon="submit" value="Upload" /></td> </tr> </table> </course> </div> </torso> </html> 6.ane. Uploading Multiple Files.
In case yous face a requirement where the client should be able to upload multiple files, everything remain the aforementioned except for 2 changes to the in a higher place example.
- We put multiple input fields within the course.
- Modify the
MultipartFile filetoMultipartFile[] files.
Let's see these lawmaking changes:
@PostMapping(value = "/upload-files") public String uploadFiles(@RequestParam("files") MultipartFile[] files, Model model) { //Logic to shop data in temp file or in DB model.addAttribute("uploadedFile", files); return "uploadForm"; } <html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <trunk> <div th:if="${uploadedFile}"> <h2> Uploaded File Details </h2> <table> <tr th:each="file: ${uploadedFile}"> <td th:text="${file.originalFilename}">File Name</td> <td thursday:text="${file.contentType}">File Type:</td> </tr> </table> </div> <div> <h2> Uploaded New File </h2> <form method="POST" enctype="multipart/form-data" action="/upload-files"> <table> <tr><td>File to upload 1:</td><td><input type="file" name="files" /></td></tr> <tr><td>File to upload 2:</td><td><input type="file" name="files" /></td></tr> <tr><td></td><td><input blazon="submit" value="Upload" /></td></tr> </table> </class> </div> </trunk> </html> 7. Testing Awarding
Nosotros completed the offset part of our post, allow's build and run our application.To start the application from command line, use mvn spring-boot:run control.Once the application is running, open the http://localhost:8080/upload-file on the browser:
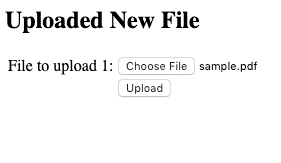
Click on the upload button, our service grade will upload the file and return the file meta-data in the response:
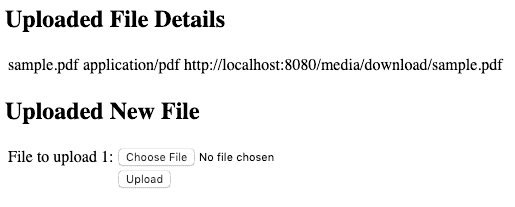
Click on the URL to download the file:
8. Jump Residuum API to upload and Download Files
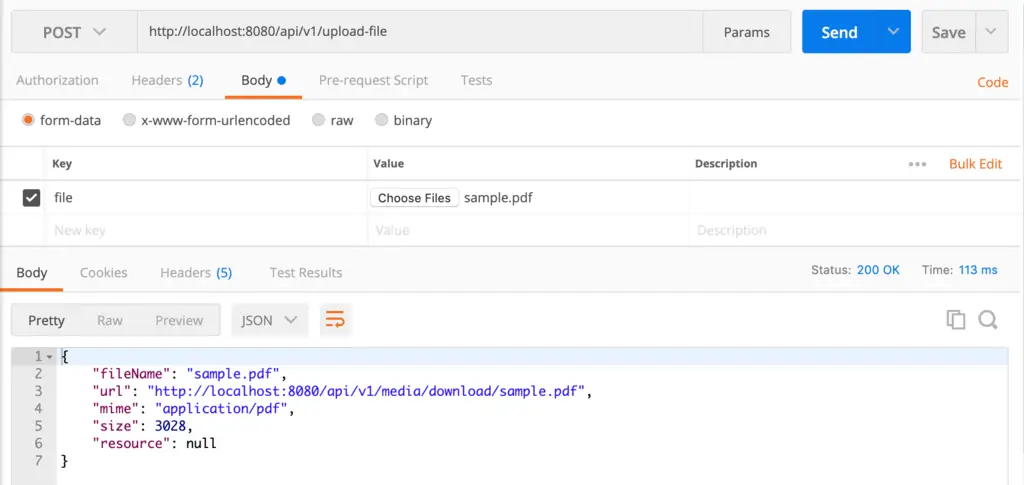
Nosotros have already completed the cadre work for our application, let's create a REST controller for uploading file with Spring Boot.We will employ Postman to test our application:
package com.javadevjournal.controller; import com.javadevjournal.data.FileMetaData; import com.javadevjournal.exception.FileStorageException; import com.javadevjournal.service.FileStorageService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity; import org.springframework.ui.Model; import org.springframework.spider web.demark.annotation.*; import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile; import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.RedirectAttributes; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; @RestController @RequestMapping("/api/v1") public class RestFileUploadController extends PageController { @Autowired FileStorageService fileStorageService; /** * Remainder controller to let file uploading for our Residuum API * @param file * @param redirectAttributes * @param model * @render FileMetaData * @throws FileStorageException */ @PostMapping("/upload-file") @ResponseBody public FileMetaData uploadFile(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file, RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes, Model model) throws FileStorageException { FileMetaData data = fileStorageService.store(file); data.setUrl(fileDownloadUrl(data.getFileName(), "/api/v1/media/download/")); return information; } /** * Residue Controller method for file download feature. * @param fileName * @return ResponseEntity * @throws FileNotFoundException */ @GetMapping("/media/download/{fileName:.+}") public ResponseEntity < Resource > downloadFile(@PathVariable String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException { FileMetaData fileData = fileStorageService.getFile(fileName); render ResponseEntity.ok() .header(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_DISPOSITION, "zipper; filename=\"" + fileName + "\"") .contentType(MediaType.parseMediaType(fileData.getMime())) .torso(fileData.getResource()); } } Our core file service will remain the aforementioned. Start the application and open the Postman or any other REST client.
Upload File:
Download File:
Click on the URL to download the file:
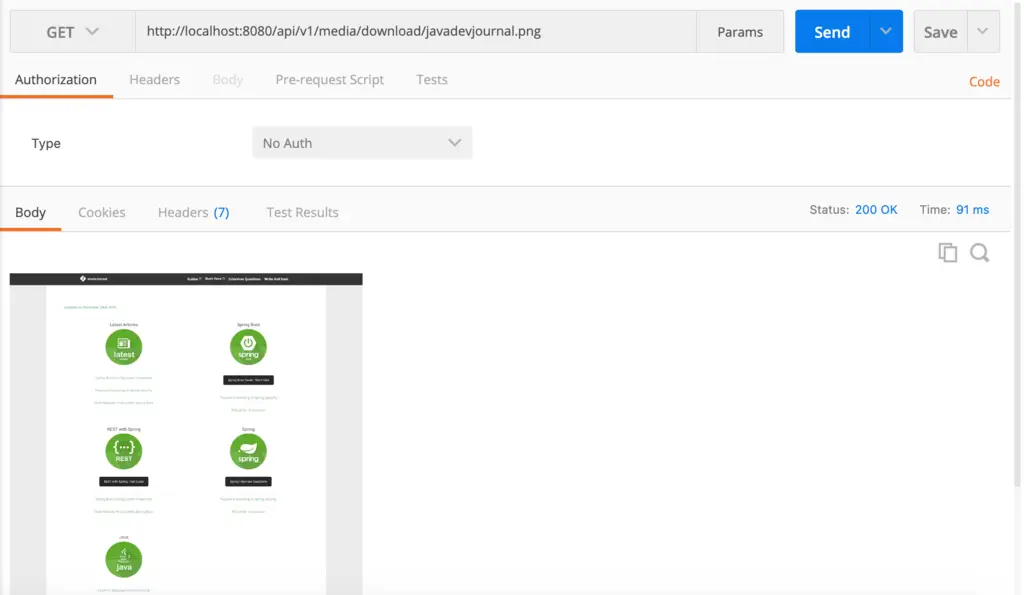
ix. Jump MVC File Upload
Well-nigh of the in a higher place concept will remain the same, even if you are non using the Leap Kick in your application. In this department, I am going to highlight the main differences or additional changes required for Bound MVC file upload.
9.1. Maven Dependencies.
We need to add the Apache Commons FileUpload dependency in our pom.xml file
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/eatables-fileupload/eatables-fileupload --> <dependency> <groupId>eatables-fileupload</groupId> <artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId> <version>one.iii.3</version> </dependency> ix.2. CommonsMultipartResolver Bean
The second footstep of our configuration involves definingCommonsMultipartResolver bean for our application. This bean is useful to customize the file upload behavior for our application.
@Edible bean public CommonsMultipartResolver multipartResolver() { CommonsMultipartResolver resolver = new CommonsMultipartResolver(); resolver.setDefaultEncoding("utf-8"); resolver.setResolveLazily(imitation); resolver.setMaxUploadSize(200000); return resolver; } 10. File Upload and Servlet 3.0
In instance you like to use Servlet iii.0 feature, you need to configure few items before using information technology. Let's see those details:
- Set a
MultipartConfigElementon the Servlet registration.
public course WebbAppInit implements WebApplicationInitializer { individual int MAX_UPLOAD_SIZE = 2 * 1024 * 1024; @Override public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException { AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext rootContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext(); rootContext.register(SpringMvcFileUploadApplication.class); // Manage the lifecycle of the root awarding context servletContext.addListener(new ContextLoaderListener(rootContext)); // Register and map the dispatcher servlet ServletRegistration.Dynamic dispatcher = servletContext.addServlet("dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet(rootContext)); dispatcher.setLoadOnStartup(i); dispatcher.addMapping("/"); MultipartConfigElement multipartConfigElement = new MultipartConfigElement("/temp", MAX_UPLOAD_SIZE, MAX_UPLOAD_SIZE * 2, 0); } } Read Jump WebApplicationInitializer for more details.
Summary
In this article, we learn the basic of uploading file with Jump Boot . We also saw the steps to upload a file in Spring MVC. Nosotros covered how you lot tin apply Leap Boot autoconfiguration to speed up the development of the file uploading features. We can find the Source code for this commodity on the GitHub.
Source: https://www.javadevjournal.com/spring/spring-file-upload/